M4 TORNADO
Element Analysis for Solids, Layers, Particles and Liquids
Configurable to Your Needs
Ultimate Speed and Accuracy

M4 TORNADO
High Performance micro-XRF with Market-Leading Speed and Flexibility

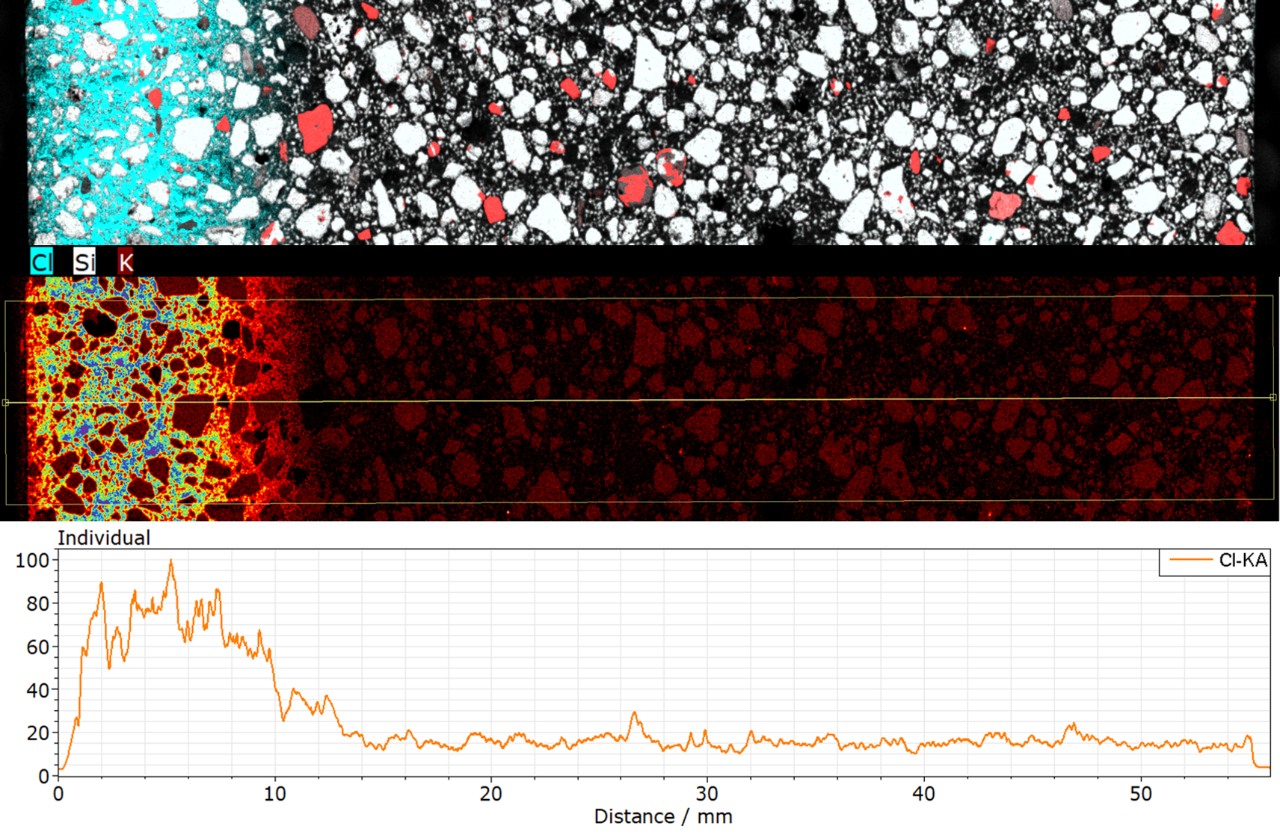
The M4 TORNADO is the tool of choice for sample characterization using small-spot micro X-ray fluorescence. Its measurements give information about composition and element distribution, even from below the surface. Bruker's micro-XRF spectrometer is optimized for high-speed analyses of points, lines and 2D area scans (element mapping) of any kind of sample; be it organic, inorganic or liquid.
The primary X-ray excitation uses a polycapillary lens offering small spot sizes and high X-ray intensity. The M4 TORNADO is configurable with a variety of Bruker XFlash® silicon drift detectors (SDD), offering high throughput without compromising energy resolution.
One of the outstanding configuration options of the M4 TORNADO is the additional X-ray tube, which offers a different target material and a collimator changer for extended analytical capabilities.
Further state-of-the-art configuration options:
- He-flush to increase light element performance while maintaining atmospheric pressure in the chamber
- A quick-exchange stage and a geo-sample holder packaged for thin sections and drill cores
- XMethod software for standard-supported and fully standard-based quantification as well as layer thickness calculation
- AMICS software for automated mineral analysis
How Can the M4 TORNADO Support Your Analyses?

Decrease measurement times. Optimized X-ray excitation path, high-throughput detectors, "on-the-fly" mapping with pixel times down to 1 ms.
Measure samples up to 7kg. Large vacuum chamber, freely adjustable, constant vacuum down to 2 mbar, automatic helium or nitrogen flush to protect your samples.
Map an area of up to 190 x 160 mm². Recording of up to 40 Mio. pixels in one run, data storage as HyperMap with full spectral information, optical image for every pixel.
Quantify spectra, linescans and mappings. Configurable fundamental parameter method, optional XMethod software package for layer or standard-based quantification, layer analysis of mappings.
Process your data. Powerful software package, extraction of arbitrary object sum spectra (ellipses, rectangles, polygons), extraction of line scans, determination of elements present only at single measurement locations (MaximumPixelSpectrum), chemical phase analysis (Autophase).
Extend your capabilities. Profit from a broad range of configurations to match your analytical needs.
Solving the Puzzle of Mineral Nutrient Homeostasis in Plants
Bruker’s M4 TORNADO Micro XRF spectrometer plays an important role in researching the role of alternative splicing (AS) mechanisms which appear to function in plant responses to environmental stress. Research scientists use the M4 TORNADO to help understand adaptive strategies used by plants to withstand a deficiency or excess of a specific mineral nutrient. This in turn helps determine ways to breed crops with higher mineral nutrient-use efficiency.